BACK PAIN AFTER A CAR ACCIDENT? WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
Every day in the United States more than 27,300 car accidents occur on the road, amounting to the staggering total of more than 10 million every single year.
Even if you drive defensively, obey speed limits and use your turn signal, it doesn’t mean everyone else on the road acts the same way. As a matter of fact, statistics show that even safe drivers are likely to experience at least 3-4 car accidents in their lifetime.
Of course, many of these accidents will be minor and do nothing but cause a little damage to your car and a headache after dealing with your insurance company.
But sometimes, accidents can be more serious.
Every year, over 2.5 million Americans visit the emergency room as a result of a car accident and in many instances, people find that they start experiencing pain in their neck or back afterward.
Many people have questions when they start feeling back pain and worry that there’s been permanent damage done to their spine. Unfortunately, much of the material that appears online (typically from law firms that are seeking to make a profit from your injury) can only fuel those fears.
In this article, we bust some of the common myths that arise around back injuries and car accidents and take a real, medical look at what can happen to your spine as the result of a crash.
WHAT’S CAUSING MY BACK OR NECK PAIN AFTER MY CAR ACCIDENT?
There are a number of painful conditions that can arise from a car accident, but they commonly stem from muscle strains or tears that occur when the head is violently thrown forward and backward; commonly known as whiplash.
Though relatively uncommon, it’s also possible to sustain injury to the spinal discs, facet joints, bone structure as as result of this motion and depending on the severity of the accident.
We’ll discuss each of these potential causes for pain in detail below:
WHIPLASH
Whiplash, otherwise known as neck strain, is one of the most common forms of neck pain that occurs after a car accident and happens when, like a whip, the head is forcibly jerked backward and then forward.
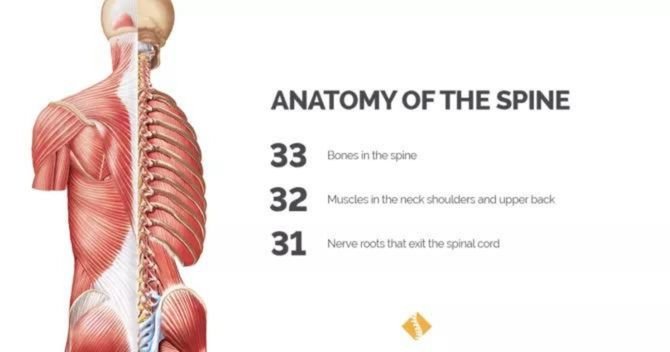
Your neck, shoulders and upper back contain 32 muscles as well as numerous tendons and ligaments that all work together to help support your spine and head. They also allow for flexibility while providing strength and movement in the neck.
These soft tissues, like others throughout the body, are susceptible to injury. What’s different about them is that they support the weight of the entire head – usually about 8 pounds – while remaining remarkably flexible.
This extensive range of motion coupled with the overall lack of stability for your head makes these muscles some of the most common to injure.
In addition to the many muscles and soft tissues that are in your neck and back, you also have your actual spine which can be susceptible to injury as well.
Your spine is made up of 33 different bones, 7 in the neck (also known as the cervical region), 12 in the thoracic region, 5 in the lumbar region, 5 in sacral region and 4 in the coccygeal region.
In addition to the bones and soft tissue, your spine has intervertebral discs between every vertebrae and 31 pairs of nerve roots that exit the spinal cord at various points.
The point is that there’s a lot in your spine that can be susceptible to injury as a result of whiplash, so there are a number of things your spine specialist should look for when investigating your pain. That said, while you should certainly have any neck or back pain examined, you should not immediately assume that chronic or permanent damage has been done to your spine as a result of your accident.
Spine and disc injury is rarely the cause of back pain, though it may often feel like it. In reality, the majority of back pain is caused by inflammation or unnecessary strain placed on the joints and muscles surrounding the spine.
WHAT HAPPENS TO MUSCLES THAT HAVE BEEN STRAINED FROM WHIPLASH?
Whiplash typically occurs when a muscle, tendon or ligament is stretched past its normal capacity, or hyperextended.
Have you ever heard of a knee hyperextending? It’s the same principle in your neck.
Your muscles, tendons and ligaments are only meant to stretch so far. For example, your arms and legs typically only stretch to a 180-degree angle.
This natural limit allows you to have incredible flexibility and movement in your extremities, while still allowing you to maintain balance and keep vital interior structures from being compressed and injured.
When, through the use of excessive force, these soft tissues are stretched beyond their capabilities the result is almost always strain of some sort.
Think about it like a rubber band. The band has a limit to how far it will naturally stretch and when it is extended beyond that point you start doing damage to the structure itself. The extent of the damage depends almost entirely on how far it is extended.
Your neck is the same way and the excessive and sudden motion of a car accident can cause the soft tissues holding it to tear on a micro level which typically produces pain, stiffness and inflammation at the site of the injury.
Other common symptoms of whiplash can include:
Headaches, especially at the base of the skull
Dizziness
Blurred vision
Constant weariness
WHAT ABOUT DIZZINESS AFTER WHIPLASH?
Muscle and soft tissue pain seems like a pretty common symptom of whiplash but, interestingly enough, about 25-50% of whiplash victims also report feeling dizzy after their accident.
Research has shown that people who have experienced whiplash can also exhibit the signs of a concussion or injury to the brain.
Concussions are caused when the brain, due to a violent blow to the head, collides with the inside of the skull. Symptoms and damage can vary depending on the severity of that impact.
People can experience dizziness, blurred vision and weariness after getting whiplash for the same reason.
Now, it’s important to note that while concussions can occur as a result of whiplash, they are relatively uncommon. The amount of force that it takes to cause a concussion is about 60g of acceleration. On the other hand, the limit of human tolerance to whiplash is only 14g.
Whiplash itself likely won’t cause a concussion on its own. Rather it could come as a result of your head hitting something, like a window or steering wheel, during the accident.
That said, people with whiplash can experience some minor concussion-like symptoms because the brain can still be impacted by the quick and forceful movement caused by the accident. However, these symptoms typically clear up within several weeks after the accident with rest and recovery.
There is still some debate in the scientific community as to why substantial inner ear problems like dizziness, ringing, vertigo and other symptoms can occur after whiplash. Some believe that the triggering of a migraine could be the cause of these symptoms.
WHAT SPINAL CONDITIONS CAN WHIPLASH CAUSE?
Most of the time, the pain caused as a result of whiplash is as a result of soft tissue injury. However, if the accident is serious enough it can cause more serious spinal conditions like a herniated disc, advanced degenerative disc disease, fractures, stenosis and others.
Disc Herniation
A herniated disc occurs when the inner, gelatinous material of the spinal disc pushes out through the rigid outer layer. This can cause pain if the fluid starts to press up against the sensitive nerve roots that exit the spine.
Herniated discs typically occur in older patients who have experienced a lifetime of natural disc degeneration. However, they can also be caused when severe amounts of pressure have been exerted on the spinal discs; often through a traumatic accident.
Symptoms of a herniated disc typically include:
Severe pain in the neck
Arm or leg pain
Tingling, numbness or weakness in the extremities (likely your arms)
Advanced Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is a natural condition that affects just about every person with a spine. It’s simply the process of your spinal discs wearing out over a lifetime of constant wear and tear.
Typically, degenerative disc disease never causes any pain and people will go their whole lives without ever knowing they have it.
However, in the case of a serious car accident, it’s possible that the spinal discs experienced a serious amount of damage and degeneration occurred at an increased rate.
Here’s a simple metaphor to help explain advanced degenerative disc disease:
Imagine a calm, quiet river. Now, we know that water is constantly eroding or “degenerating” the banks of the river. Over time, the river will become wider and deeper as erosion naturally continues.
Now, imagine that one day there’s a flash flood and a ton of water rushes through quiet river. Suddenly, erosion is going to occur at a much quicker rate than it naturally would.
This is similar to what can happen to your spinal discs during an accident. Over the course of your life, your discs will naturally erode or degenerate. However, whiplash is like a flash flood pouring through your spine and putting a ton of extra pressure and force on your discs, causing dengeration to happen at a much quicker rate.
Degenerative disc disease can cause a number of different conditions including spinal stenosis, bone spurs, disc herniation and more.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the canal that houses the spinal cord and nerves narrows as a result of bone spurs or thickened ligaments.
Stenosis typically occurs when the spine has been destabilized by some sort of injury or degeneration. To combat excess movement and to compensate for degeneration, the body will naturally build up bone spurs or thicken the ligaments around the area. A side effect of this process is a narrowing of the spinal canal and potentially pressure being placed on the vital nerves that run through it.
Symptoms of spinal stenosis typically include:
Weakness or tingling in the arms
Difficulty balancing or standing
It’s important to note that while stenosis has been reported in patients who have experienced whiplash, there hasn’t been a direct correlation as of yet.
Facet Joint Disease
Facet joint disease is a condition where the facet joints in the spine degenerate to the point of causing pain.
Facet joints run all the way up the spine and allow for movement and flexibility in the back. Similar to other major joints in the body like the knees and shoulders, these joints are lined with cartilage that can naturally wear out over time.
However, like degenerative disc disease, this process can be expedited by significant trauma to the spine; like whiplash.
The symptoms and amount of pain a person experiences from facet disease depends almost entirely on the location of the degenerated joint, the extent of damage that has occurred and the amount of pressure that it is putting on the surrounding nerve roots.
For example, a degenerated joint in the upper spine will generally manifest itself through symptoms in the neck, shoulders and, occasionally, headaches.
Conversely, symptoms from a damaged joint in the middle or lower back will typically be felt in the lower back, buttocks or legs. That said, there are some common symptoms that do occur in patients with facet disease, these include:
Throbbing lower back pain that radiates into the buttocks or upper thighs
Pain that goes from the back of the neck out to the shoulders
Bone spurs
Inflammation
Tenderness of certain areas of the spine
Pain that is exasperated through certain spine movements, like twisting your back, bending over, leaning back, etc.
WHEN SHOULD I SEE A DOCTOR AS A RESULT OF WHIPLASH?
Most cases of whiplash, while potentially painful, will heal on their own. However, if you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms for an extended period of time, you should see a spinal specialist:
Symptoms spread to the shoulders or arms
Moving your head is exceptionally painful and not getting better with time
You feel a bulge in your neck
You have numbness or weakness in your arms
Often, these types of symptoms are indicative of a more serious problem with the spinal structure itself, likely a herniated disc that is pressing up against the nerve roots that exit your spine. It could also be an indication of damage to the vertebrae itself or the tendon or ligament structures that are connected to the bones.
Regardless of whether or not you are experiencing these more serious symptoms of whiplash, you should always see your spinal specialist after experiencing any kind of trauma to the head or neck that is causing you prolonged discomfort or pain.
Oftentimes, we are not the best judges of our pain and far too often we assume that problems will simply go away on their own. While this is true in most cases, there are instances where medical attention is required and it is always far better to receive that attention as early as possible to avoid any permanent damage.
WILL MY WHIPLASH PAIN GO AWAY?
In most cases, the pain from whiplash typically goes away after about 6 weeks. However, a vast majority of the pain should dissipate a couple of days after the accident as the soft tissues impacted begin to heal and inflammation dies down.
While painful, whiplash typically doesn’t affect the vital nerves, bones or other structures located within the neck and pain can be reduced with ice, pain-relieving medication and rest.
Which means that the prognosis for victims of whiplash is often good, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
That said, about 12-50% of people still report experiencing symptoms, like headaches or neck pain, after a year and others will continue to exhibit symptoms the rest of their lives.
The amount of time that pain lasts is typically dependent on the seriousness of the accident, the amount of damage that was caused to the spine and soft tissues and whether or not you had any preexisting spinal conditions beforehand.
By taking a MRI or CT-scan of your spine, a neurosurgeon will be able to better determine the symptoms that you’ll likely experience as you’re recovering from your accident and whether or not they will be long-term.
HOW IS WHIPLASH TREATED?
Typically, the best treatment for whiplash is simply rest. Your neurosurgeon may prescribe you an over-the-counter medication like Tylenol or aspirin to help with pain while more serious cases may require muscle relaxants or stronger painkillers.
Apart from using medication sparingly, you can combat your back or neck pain using at-home, conservative treatments.
If the muscles in your neck are tight or knotted after your accident, you can apply local heat therapy to the area to help encourage blood flow to the area. When applying heat, you should first determine which muscles are tight, then heat up that area of your body using a warm water bottle, a heating pad or a heated gel pack onto the affected muscle. Depending on the severity of your strain, you can leave the heat on for 20-30 minutes (minor strain) to up to 2 hours (severe strain).
If your neck injury is considered “fresh”, meaning that it is swollen, red, hot or bruised, apply an ice pack to the area for no more than 20 minutes.
This will help restrict blood flow to the area and help relieve swelling and inflammation pain.
Your spine specialist may also recommend that you visit a chiropractor or a masseuse to help adjust your spine or loosen the muscles surrounding it to help provide some pain relief.
CONCLUSION
Rest is typically the best way to help you recover from whiplash but, nevertheless, it may be helpful to visit a spine specialist after undergoing a car accident just to ensure that everything in your spine and neck is without injury.
Symptoms of a more serious spine injury can sometimes take days, even weeks, to fully manifest, but can be caught early through tests and imaging. Even if there isn’t an injury a spinal scan can give you the peace of mind to know that, with time, your pain will very likely decrease.
Have more questions about your spine pain or want to get your neck examined by our neurosurgeon? Just contact us and we’ll help you schedule your initial consultation.